Credit Reporting Act 2013
Number 45 of 2013
CREDIT REPORTING ACT 2013
REVISED
Updated to 28 August 2019
This Revised Act is an administrative consolidation of the Credit Reporting Act 2013. It is prepared by the Law Reform Commission in accordance with its function under the Law Reform Commission Act 1975 (3/1975) to keep the law under review and to undertake revision and consolidation of statute law.
All Acts up to and including the Judicial Council Act 2019 (33/2019), enacted 23 July 2019, and all statutory instruments up to and including the Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 20) (Verification of Identity of Credit Information Subjects) (Amendment) Regulations 2019 (S.I. No. 433 of 2019), made 28 August 2019, were considered in the preparation of this Revised Act.
Disclaimer: While every care has been taken in the preparation of this Revised Act, the Law Reform Commission can assume no responsibility for and give no guarantees, undertakings or warranties concerning the accuracy, completeness or up to date nature of the information provided and does not accept any liability whatsoever arising from any errors or omissions. Please notify any errors, omissions and comments by email to
revisedacts@lawreform.ie.

Number 45 of 2013
CREDIT REPORTING ACT 2013
REVISED
Updated to 28 August 2019
CONTENTS
Preliminary and General
Section
1. Short title and commencement
The Central Credit Register
8. Period for which information may be held on Register
9. Application for amendment of information held on Register
10. Notification of decision on application for amendment
11. Duty of credit information provider to provide information for Register
12. Duty to provide information about foreign credit
13. Statement explaining information
14. Duty to access information on Register
15. Power to access information on Register
16. Purposes for which information may be used by credit information provider
17. Access to Register: supplementary
18. Notices of suspected impersonation
Duties of Credit Information Providers
20. Verification of identity of credit information subjects
21. Verification of accuracy of credit information
22. Informing credit information subject of suspected impersonation
23. Ensuring that credit information subjects are aware of rights and duties
24. Informing credit information subjects of duty to provide information
Levy and Fees
25. Levy on credit information providers
Enforcement
28. Enforcement: supplementary
Miscellaneous
30. Power of Bank to produce credit scores and anonymised information
32. Prohibition on unauthorised disclosure of information
34. Amendment of section 33AK of Central Bank Act 1942
35. Amendment of section 5 of Central Bank (Supervision and Enforcement) Act 2013
Acts Referred to
Central Bank (Supervision and Enforcement) Act 2013 (No. 26)
Central Bank Act 1942 (No. 22)
Companies Act 1963 (No. 33)
Data Protection Act 1988 (No. 25)
Data Protection Acts 1988 and 2003
Fiscal Responsibility Act 2012 (No. 39)
Local Government Act 2001 (No. 37)
National Asset Management Agency Act 2009 (No. 34)
Pawnbrokers Act 1964 (No. 31)

Number 45 of2013
CREDIT REPORTING ACT 2013
REVISED
Updated to 28 August 2019
An Act to make provision for the establishment, maintenance and operation of a central credit register for the holding of information about credit applications and credit agreements and parties to them; to make provision about the information to be provided for entry on the register; to make provision for access to the information held on the register for the assessment of creditworthiness and other purposes; to impose duties on parties to credit agreements; to amend the Central Bank Act 1942; and the Central Bank (Supervision and Enforcement) Act 2013; and to make provision for related matters.
[23rd December, 2013]
Be it enacted by the Oireachtas as follows:
Annotations
Editorial Notes:
E1
Central Bank excluded from definition of public bodies in Freedom of Information Act 2014 (30/2014) in so far as it relates to certain records of this Act (14.10.2014) by Freedom of Information Act 2014 (30/2014), s. 6 and sch. 1 part 1(b)(ii), commenced as per s. 1(2).
PART 1
Preliminary and General
 Section 1
Section 1
Short title and commencement
1. (1) This Act may be cited as the Credit Reporting Act 2013.
(2) This Act comes into operation on such day or days as the Minister may appoint by order or orders either generally or with reference to any particular purpose or provision, and different days may be so appointed for different purposes or different provisions.
Annotations
Editorial Notes:
E2
Power pursuant to subs. (2) exercised (27.01.2014) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Commencement) Order 2014 (S.I. No. 19 of 2014).
2. The 27th day of January 2014 is appointed as the day on which the Credit Reporting Act 2013 (No. 45 of 2013) comes into operation.
 Section 2
Section 2
Interpretation
2. (1) In this Act—
“anonymised information” has the meaning given by section 5(3);
“Bank” means the Central Bank of Ireland;
“consumer price index” means the Consumer Price Index (All Items) published by the Central Statistics Office or any equivalent index published from time to time by that Office;
“credit” includes a loan, deferred payment or other form of financial accommodation, other than any provided—
(a) by one credit institution to another,
(b) to any entity classified within general government in relation to the State within the meaning given by the Fiscal Responsibility Act 2012, the government of any other country or territory or any international organisation,
(c) by a company to a related undertaking of the company,
(d) by a person who does not provide credit except to the person’s employees,
(e) in connection with the provision of a utility or other service on a continuing basis,
F1[(f) in the form of trade credit, or]
(g) without any requirement to pay interest or any other charge (in any circumstances);
“credit agreement” means, subject to subsection (2), an agreement made between a credit information provider and another person for the provision of credit for the other person;
“credit application” means, subject to subsection (2), an application for the provision of credit made to a credit information provider and completed in accordance with the application processes of the credit information provider;
“credit information” has the meaning given by section 7;
“credit information provider” means, subject to subsection (3)—
(a) a regulated financial services provider,
(b) NAMA,
(c) a local authority, or
(d) any person not within paragraphs (a) to (c) who provides credit, other than—
(i) the Bank or the central bank of any country or territory other than the State, or
(ii) a pawnbroker, within the meaning of the Pawnbrokers Act 1964;
“credit information subject” means a person who—
(a) has made a credit application,
(b) has made a credit agreement for the provision of credit to the person, or
(c) is a guarantor;
“credit institution” means a credit institution within the meaning of Article 4.1(1) of Regulation (EU) No. 575/2013 1 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 June 2013 on prudential requirements for credit institutions and investment firms and amending Regulation (EU) No. 648/2012;
“credit score”, in relation to a credit information subject, means a numerical or alphanumerical value assigned to the credit information subject, on the basis of information on the Register relating to the credit information subject, to indicate the level of risk of the credit information subject defaulting on financial obligations;
“Governor” has the meaning given by section 2(1) of the Central Bank Act 1942;
“guarantor” means a person who is proposing to give, or has given, a guarantee or indemnity in connection with a credit agreement;
“Head of Function” has the meaning given by section 2(1) of the Central Bank Act 1942;
“international organisation” has the meaning given by section 186B of the Social Welfare Consolidation Act 2005;
“local authority” has the meaning given by section 2(1) of the Local Government Act 2001;
“Minister” means the Minister for Finance;
“NAMA” means the National Asset Management Agency;
“notice” means a notice given in writing (whether electronically or otherwise);
“personal information” has the meaning given by section 6;
“qualifying credit agreement” has the meaning given by section 11(5);
“qualifying credit application” has the meaning given by section 11(5);
“Register” means the Central Credit Register established under section 5;
“regulated financial services provider” has the meaning given by section 2(1) of the Central Bank Act 1942;
“related undertaking”, in relation to a company, means—
(a) a subsidiary of the company,
(b) the holding company of the company,
(c) a subsidiary of—
(i) the holding company of the company, or
(ii) a subsidiary of that holding company,
and for this purpose “holding company” and “subsidiary” have the meanings given by section 155 of the Companies Act 1963;
“relevant credit application” has the meaning given by section 14(5).
F2[(1A) For the purposes of paragraph (f) of the definition of ‘credit’ in subsection (1), a loan, deferred payment or other form of financial accommodation (the ‘relevant credit’) is provided in the form of trade credit if the following conditions are satisfied—
(a) in the case of both the person (the ‘first-mentioned person’) by whom, and the person to whom, the relevant credit is provided, each is acting in the course of his or her business, trade or profession,
(b) the first-mentioned person is not a regulated financial services provider,
(c) the terms of the relevant credit provide for repayment, whether in instalments or as a single amount, of the whole of the credit by a date that is not later than 6 months after the date of its provision, and
(d) the purpose of the relevant credit is to facilitate the purchase of goods or services from the first-mentioned person.]
(2) A credit application or credit agreement is not one in relation to which this Act applies unless—
(a) the applicant for the provision of credit, or the person for whom credit is provided under the credit agreement, is resident in the State at the time when the credit application or credit agreement is made, or
(b) the law governing any credit agreement made pursuant to the application would be, or the law governing the credit agreement is, the law of the State.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), where a person has acquired rights of a credit information provider under a credit agreement, for the purposes of this Act that person is with respect to the rights acquired the credit information provider in relation to the credit agreement, instead of the person whose rights under the credit agreement have been acquired.
(4) Subsection (3) does not apply in relation to a credit agreement where a participating institution is performing any relevant service in respect of rights under the credit agreement pursuant to an arrangement or agreement under section 131 of the National Asset Management Agency Act 2009.
(5) In subsection (4)—
“participating institution” has the meaning given by section 4(1) of the National Asset Management Agency Act 2009;
“relevant service” has the meaning given by section 128 of the National Asset Management Agency Act 2009.
Annotations
Amendments:
F1
Substituted (29.10.2018) by Markets in Financial Instruments Act 2018 (25/2018), s. 8(a), commenced on enactment.
F2
Inserted (29.10.2018) by Markets in Financial Instruments Act 2018 (25/2018), s. 8(b), commenced on enactment.
 Section 3
Section 3
Regulations and orders
3. (1) Any regulations made by the Bank or order made by the Minister under this Act may contain such incidental, supplementary or consequential provisions as appear to the Bank or the Minister to be necessary or expedient for the purposes of the regulations or order.
(2) Any regulations or order made under this Act, other than an order under section 1(2), shall be laid before each House of the Oireachtas as soon as may be after being made and, if a resolution annulling the regulations or order is passed by either such House within the next 21 days on which that House has sat after the regulations are or order is laid before it, the regulations or order shall be annulled accordingly, but without prejudice to the validity of anything previously done under the regulations or order.
 Section 4
Section 4
Expenses
4. The expenses incurred by the Minister in the administration of this Act shall, to such extent as may be sanctioned by the Minister for Public Expenditure and Reform, be paid out of moneys provided by the Oireachtas.
PART 2
The Central Credit Register
 Section 5
Section 5
Central Credit Register
5. (1) The Bank shall establish, maintain and operate a database of information to be known as the Central Credit Register (referred to in this Act as the “Register”).
(2) The Bank may hold on the Register—
(a) personal information in relation to a credit information subject,
(b) credit information which relates to any credit application or credit agreement made by a credit information subject or any credit agreement in connection with which the credit information subject is a guarantor,
(c) details linking any credit information subject who has made a credit agreement for the provision of credit with any other credit information subject who has given a guarantee or indemnity in connection with the credit agreement or also has liabilities under the credit agreement, and
(d) credit scores and other analyses produced by the Bank in relation to a credit information subject.
(3) The credit information that the Bank may hold on the Register also includes general reports, analyses and statistics produced by the Bank from which credit information subjects cannot be identified (referred to in this Act as “anonymised information”).
 Section 6
Section 6
Personal information
6. (1) In relation to a credit information subject who is an individual, the following is personal information—
(a) the individual’s forename and surname and any former surnames (including any alias);
(b) the individual’s mother’s birth surname;
(c) the individual’s date and place of birth;
(d) the individual’s address and previous addresses;
(e) the individual’s telephone number;
(f) the individual’s personal public service number (within the meaning of section 262 of the Social Welfare Consolidation Act 2005) and any other reference numbers allocated to the individual for the purposes of tax (whether in the State or any other country or territory);
(g) the individual’s employment status and, if employed or carrying on other activities, the individual’s occupation and the sector of the economy in which the individual is occupied.
(2) In relation to a credit information subject who is an individual carrying on activities otherwise than as an employee, the following is also personal information—
(a) any trading name, the nature of the entity by which the activities are carried on and any registration number issued to the credit information subject by the Companies Registration Office;
(b) the address of the place (or, where more than one, the principal place) at which the activities are carried on;
(c) the telephone number for any place where the activities are carried on.
(3) In relation to a credit information subject which is not an individual, the following is personal information—
(a) the credit information subject’s name, the nature of the entity it is and any registration number issued to it by the Companies Registration Office;
(b) the address of the place (or, where more than one, the principal place) at which the activities of the credit information subject are carried on and (if a company) the address of the registered office of the credit information subject;
(c) the telephone number of the credit information subject;
(d) all reference numbers allocated to the credit information subject for the purposes of tax (whether in the State or any other country or territory);
(e) the sector of the economy in which the credit information subject carries on its activities.
(4) The Bank may, following consultation with the Data Protection Commissioner and with the consent of the Minister, make regulations specifying additional information which is to be personal information in relation to all credit information subjects or in relation to any class of credit information subjects.
(5) Regulations under subsection (4) may not be made unless the Bank considers that the holding on the Register of the personal information specified in the regulations is likely to facilitate the accurate identification of credit information subjects.
(6) A person who uses, or seeks to have disclosed, a personal public service number for any purpose connected with this Act does not commit an offence under section 262(9) of the Social Welfare Consolidation Act 2005.
Annotations
Modifications (not altering text):
C1
References to Data Protection Commissioner construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), s. 14(2), commenced as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 175 of 2018.
Transfer of functions of Data Protection Commissioner to Commission
14. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the Data Protection Commissioner are transferred to the Commission.
(2) A reference in any enactment or instrument under an enactment to the Data Protection Commissioner or to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner shall be construed as a reference to the Commission.
...
Editorial Notes:
E3
Power pursuant to subs. (4) exercised (30.06.2017) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 6) (Additional Personal Information) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 485 of 2016), in effect as per reg. 1(2).
 Section 7
Section 7
Credit information
7. (1) The following is credit information in relation to a credit application or credit agreement made by a credit information subject or a credit agreement in connection with which a credit information subject is a guarantor—
(a) the nature and term of the credit applied for or agreed (including the amount or maximum amount of credit, the currency in which it is denominated and conditions about payment or repayment);
(b) the nature and extent of any guarantee or indemnity, or any security, given or to be given and details of any associated valuation;
(c) the rate or rates of interest payable or to be payable;
(d) any identifying number allocated to the credit application or credit agreement, or to the credit information subject, by the credit information provider;
(e) details of any risk rating undertaken in relation to the credit applied for or agreed;
(f) details of any securitisation of the credit agreed.
(2) The following is also credit information in relation to a credit agreement made by a credit information subject or a credit agreement in connection with which a credit information subject is a guarantor—
(a) any changes to the nature or term of the credit agreed or to any guarantee, indemnity or security given in connection with the credit agreement;
(b) any proposal or arrangement with respect to debts under the credit agreement or any guarantee or indemnity given in connection with the credit agreement;
(c) other information relating to the performance of obligations under or relating to the credit agreement or any guarantee or indemnity given in connection with the credit agreement.
(3) The Bank may, following consultation with the Data Protection Commissioner and with the consent of the Minister, make regulations specifying additional information relating to credit applications or credit agreements, or any class of credit applications or credit agreements, which is to be credit information in relation to credit applications or credit agreements or that class of credit applications or credit agreements.
(4) Regulations under subsection (3) may not be made unless the Bank considers that the holding on the Register of the credit information specified in the regulations is likely to facilitate the making by credit information providers of decisions whether to provide credit or on what terms or the performance by the Bank of any of its functions.
Annotations
Modifications (not altering text):
C2
Reference to Data Protection Commissioner construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), s. 14(2), commenced as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 175 of 2018.
Transfer of functions of Data Protection Commissioner to Commission
14. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the Data Protection Commissioner are transferred to the Commission.
(2) A reference in any enactment or instrument under an enactment to the Data Protection Commissioner or to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner shall be construed as a reference to the Commission.
...
 Section 8
Section 8
Period for which information may be held on Register
8. (1) Personal information and credit information which identifies a credit information subject and is held on the Register as the result of a credit application may be held on the Register for 6 months beginning with the day on which it is entered on the Register.
(2) Personal information and credit information which identifies a credit information subject and is held on the Register as the result of a credit agreement may be held on the Register—
(a) in the case of credit information to which section 7(2)(b) applies, until the end of the period of 5 years beginning with the day on which the proposal is withdrawn or the arrangement is terminated,
(b) in the case of credit information to which section 5(2)(d) or 7(2)(c) applies, until the end of the period of 5 years beginning with the day on which it is entered on the Register,
(c) in the case of any other credit information, until the end of the period of 5 years beginning with the first day on which all liabilities under the credit agreement to which it relates have been discharged, and
(d) in the case of personal information, for as long as any credit information relating to the credit information subject may be held on the Register.
(3) Anonymised information may be held on the Register indefinitely.
 Section 9
Section 9
Application for amendment of information held on Register
9. (1) Where the Bank receives an application from a credit information provider or credit information subject to amend information held on the Register on the ground that it is inaccurate, incomplete or not up to date, the Bank—
(a) shall take all such steps, including giving notice requiring the provision of information from any credit information provider or credit information subject, as are reasonable to enable the Bank to decide whether to amend the information, and
(b) where it decides that the information should be amended, shall do so.
(2) An application under subsection (1) shall be in writing and accompanied by information supporting the application.
(3) Where the Bank requires a credit information provider or credit information subject to provide information under subsection (1)(a), the requirement shall be complied with within 15 days of the date on which the notice is received.
(4) If an application under subsection (1) is made by a credit information subject, the Bank shall, unless the application has already been decided or withdrawn, notify the credit information subject that the Bank will, no later than 20 days after the date on which the application is received, give notice to the credit information subject either—
(a) of the decision that has been made on the application, or
(b) that the Bank requires until such date as is specified in the notice, not being more than 40 days after the date on which the application is received, to make a decision on the application.
(5) If an application under subsection (1) is made by a credit information subject, the Bank shall, unless the application has already been decided or withdrawn, make a decision on the application no later than 20 days after the date on which the application is received or, if the Bank gives notice under subsection (4)(b), no later than the date specified in the notice.
(6) If the Bank gives notice to a credit information subject under subsection (4)(b), the notice shall state the reasons why it has not yet been possible to make a decision.
(7) Where an application to access information held on the Register which relates to a credit information subject is made at a time when an application to amend the information has been made but not decided, the Bank shall either—
(a) refuse to give access to the information until the application to amend the information has been decided, or
(b) indicate to the person making the application to access the information that an application to amend the information has been made but not decided.
 Section 10
Section 10
Notification of decision on application for amendment
10. (1) If the Bank decides to amend information held on the Register in consequence of an application under section 9(1), the Bank shall give notice of the decision together with a copy of the amended information to—
(a) the credit information subject to whom the information relates,
(b) if the application was made by a credit information provider, that credit information provider,
(c) if the information relates to a credit agreement the term of which has not come to an end, any person who is a party to the credit agreement, and
(d) any credit information provider who has, since the relevant date, made an application to access information relating to the credit information subject which is held on the Register.
(2) In subsection (1)(d) “relevant date” means the date that is 12 months before the date on which the application was received or (if later) the date on which information relating to the credit information subject was first held on the Register.
(3) If the Bank decides not to amend information held on the Register in consequence of an application under section 9(1), the Bank shall inform the applicant of the decision and, in the case of an application by a credit information subject, shall, if requested to do so by the credit information subject, enter on the Register (alongside the information) a statement of the amendment sought.
 Section 11
Section 11
Duty of credit information provider to provide information for Register
11. (1) A credit information provider shall provide to the Bank—
(a) such personal information and credit information relating to any qualifying credit application made to the credit information provider, and to the credit information subject by whom any such application was made, as is required to be provided by regulations under subsection (2), and
(b) such personal information and credit information relating to any qualifying credit agreement made by the credit information provider, and to the credit information subject with whom the qualifying credit agreement was made or any credit information subject who is a guarantor in connection with the credit agreement, as is so required.
(2) The Bank shall, with the consent of the Minister, make regulations specifying—
(a) the information that is to be provided to the Bank under subsection (1),
(b) the form in which, and when, that information is to be so provided, and
(c) requirements as to verification which are to be met or complied with in connection with that information.
(3) Regulations under subsection (2) may make different provision in relation to different classes of—
(a) qualifying credit applications,
(b) qualifying credit agreements,
(c) credit information providers, and
(d) credit information subjects.
(4) The Bank may include information provided under this section on the Register.
(5) A credit application or credit agreement is a qualifying credit application or qualifying credit agreement for the purposes of this Act if the amount of the credit applied for or agreed to be provided is at least the amount provided for by subsection (6).
(6) The amount referred to in subsection (5) is—
(a) such amount as is for the time being specified by order under subsection (7), or
(b) where no amount is for the time being so specified, €500.
(7) The Minister may, from time to time, review the amount for the time being provided for by subsection (6) and may, following consultation with the Bank and having regard to changes in the consumer price index, the implications for the effective and efficient operation of the Register and the effect on credit information providers and credit information subjects, by order specify a different amount instead of that amount.
(8) The Minister may revoke an order under subsection (7) without specifying another amount (in which case the amount specified in paragraph (b) of subsection (6) is the amount provided for by that subsection).
Annotations
Editorial Notes:
E4
Power pursuant to section exercised (30.06.2017) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 11) (Provision of Information for Central Credit Register) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 486 of 2016), in effect as per reg. 1(2).
 Section 12
Section 12
Duty to provide information about foreign credit
12. (1) A credit information subject who makes a credit application to a credit information provider shall, on making the application, give notice to the credit information provider if the credit information subject has an outstanding aggregate debt of more than €5,000 under agreements that would be credit agreements but for section 2(2).
(2) The Bank may, with the consent of the Minister, make regulations specifying—
(a) the information that is to be provided in a notice under subsection (1), and
(b) the form in which, and when, that information is to be so provided.
(3) A credit information provider who receives a notice under subsection (1) shall provide the information contained in it to the Bank together with a statement that the information has been provided in compliance with such a notice.
(4) The Bank may include information and statements received by the Bank under subsection (3) on the Register.
(5) The Minister may, from time to time, review the amount for the time being specified in subsection (1) and may, following consultation with the Bank and having regard to changes in the consumer price index, the implications for the effective and efficient operation of the Register and the effect on credit information providers and credit information subjects, by order specify a different amount instead of that amount.
(6) The Minister may revoke an order under subsection (5) without specifying another amount (in which case the amount specified in subsection (1) is €5,000).
 Section 13
Section 13
Statement explaining information
13. (1) A credit information subject may by notice to the Bank give a statement of not more than 200 words relating to any information held on the Register which relates to the credit information subject.
(2) The Bank shall include on the Register any statement made under subsection (1).
 Section 14
Section 14
Duty to access information on Register
14. (1) A credit information provider shall make an application to access information held on the Register which relates to a person who has made a relevant credit application to the credit information provider.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply if the credit information provider has made an application to access the information not more than 7 days before the relevant credit application is made.
(3) Subsection (1) shall be complied with no later than the date on which a decision whether to provide credit is made in response to the relevant credit application.
(4) Information accessed as the result of an application under subsection (1) may be used by the credit information provider only for a purpose specified in section 16.
(5) A credit application is a relevant credit application for the purposes of this Act if the amount of the loan or facility applied for is at least the amount provided for by subsection (6).
(6) The amount referred to in subsection (5) is—
(a) such amount as is for the time being specified by order under subsection (7), or
(b) where no amount is for the time being so specified, €2,000.
(7) The Minister may, from time to time, review the amount for the time being provided for by subsection (6) and may, following consultation with the Bank and having regard to changes in the consumer price index, the implications for the effective and efficient operation of the Register and the effect on credit information providers and credit information subjects, by order specify a different amount instead of that amount.
(8) The Minister may revoke an order under subsection (7) without specifying another amount (in which case the amount specified in paragraph (b) of subsection (6) is the amount provided for by that subsection).
 Section 15
Section 15
Power to access information on Register
15. (1) A credit information provider may make an application to access information held on the Register which relates to a person who—
(a) has made to the credit information provider a credit application that is not a relevant credit application, or
(b) is proposing to give a guarantee or indemnity in connection with a credit application made to the credit information provider.
(2) A credit information provider may make an application to access any information held on the Register which relates to a person who is a credit information subject in relation to a credit agreement made with the credit information provider if that person, or any other person who is a credit information subject in relation to the credit agreement—
(a) has requested the credit information provider to change the nature or term of the credit agreement or a guarantee or indemnity given in connection with the credit agreement or has requested any other credit information provider to change the nature or term of any other credit agreement or a guarantee or indemnity given in connection with any other credit agreement, or
(b) has failed to comply with any obligation under the credit agreement or any other credit agreement made with any other credit information provider or a guarantee or indemnity given in connection with the credit agreement or any other such credit agreement and that failure has not been corrected.
(3) A credit information provider may make an application to access any information held on the Register which relates to the credit agreements made by the credit information provider.
(4) Information accessed as the result of an application under subsection (1), (2) or (3) may be used by the credit information provider only for a purpose specified in section 16.
(5) A credit information subject may make an application to access information held on the Register which relates to the credit information subject.
(6) Any person may make an application to access information held on the Register which relates to a credit information subject with the consent of the credit information subject.
(7) The Bank may use any information held on the Register in the performance of any of its functions.
 Section 16
Section 16
Purposes for which information may be used by credit information provider
16. The purposes referred to in sections 14(4) and 15(4) are—
(a) verifying information provided in or in connection with a credit application;
(b) evaluating any risk arising from the affording or extending of credit to, or the taking of a guarantee or indemnity from, a credit information subject;
(c) evaluating any risk arising from any changes to the nature or term of a credit agreement, or to a guarantee or indemnity given in connection with a credit agreement;
(d) monitoring any failure to comply with any obligation under a credit agreement or a guarantee or indemnity given in connection with a credit agreement that has not been corrected;
(e) evaluating whether to make any proposal or arrangement with respect to the debts of a credit information subject in circumstances in which a credit information subject has made a request for such an evaluation to be made;
(f) analysing the nature of the credit information provider’s portfolio of credit agreements.
 Section 17
Section 17
Access to Register: supplementary
17. (1) The Bank shall, following consultation with the Data Protection Commissioner and with the consent of the Minister, make regulations which make provision about—
(a) applications to access information under section 14 or 15,
(b) the information to which the Bank is to be required to give access in response to such applications,
(c) when access to the information is to be given, and
(d) the manner in which access to the information is to be given.
(2) Regulations under subsection (1) may make different provision in relation to—
(a) different classes of persons who are applicants to access information held on the Register, or
(b) different descriptions of information so held.
(3) A credit information provider shall keep for 5 years a record of each occasion on which the credit information provider has been given access to information held on the Register under section 14 or 15.
(4) A credit information provider shall, if required to do so by the Bank, provide to the Bank information about any occasion on which the credit information provider has been given access to information held on the Register in response to an application under section 14 or 15.
(5) The Bank shall keep for 5 years a record of each occasion on which access has been given to information held on the Register in response to an application under section 14 or 15.
(6) A credit information subject may by notice to the Bank require the Bank to provide a record of—
(a) each occasion on which access has been given to information held on the Register which relates to the credit information subject in response to applications made under section 14 or 15 within the period of 5 years ending with the day on which the notice is given,
(b) the identity of the persons by whom the applications were made, and
(c) the dates on which they were made.
Annotations
Modifications (not altering text):
C3
References to Data Protection Commissioner construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), s. 14(2), commenced as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 175 of 2018.
Transfer of functions of Data Protection Commissioner to Commission
14. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the Data Protection Commissioner are transferred to the Commission.
(2) A reference in any enactment or instrument under an enactment to the Data Protection Commissioner or to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner shall be construed as a reference to the Commission.
...
Editorial Notes:
E5
Power pursuant to section exercised (31.12.2017) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 17) (Access to Central Credit Register) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 487 of 2016), in effect as per reg. 1(2).
 Section 18
Section 18
Notices of suspected impersonation
18. (1) Where a credit information subject gives notice to the Bank that the credit information subject reasonably believes that the credit information subject may have been, may be being or may be about to be impersonated by any person, the Bank shall enter a notice of suspected impersonation on the Register as soon as is reasonably practicable and (in any event) within 48 hours of receiving the notice.
(2) The Bank shall remove the notice of suspected impersonation if the credit information subject gives it notice requiring it to do so.
(3) Subject to subsection (2), the Bank shall remove the notice of suspected impersonation at the end of the period of 90 days beginning with the day on which it is entered on the Register unless the credit information subject gives notice before the end of that period requiring the Bank to retain it.
(4) Where notice is given under subsection (3) the Bank shall, subject to subsection (2), retain the notice of suspected impersonation for the period specified in the notice under subsection (3) or (if shorter) the period of 90 days beginning with the day on which it would otherwise be removed under subsection (3).
(5) Where a notice of suspected impersonation of a credit information subject is entered on the Register, the Bank shall notify the credit information subject as soon as is reasonably practicable and (in any event) within 48 hours if—
(a) an application is made to access information held on the Register which relates to the credit information subject, or
(b) information is provided to the Bank in consequence of a credit application or credit agreement made by the credit information subject.
(6) Where the Bank gives any person access to information held on the Register which relates to a credit information subject at a time when a notice of suspected impersonation of the credit information subject is held on the Register, the Bank shall bring the notice to the person’s attention.
 Section 19
Section 19
Data protection
19. (1) Nothing in this Act limits the operation of the Data Protection Acts 1988 and 2003.
(2) Sections 2, 4 and 6 of the Data Protection Act 1988 shall have effect as if—
(a) references to personal data included relevant credit data, and
(b) a person to whom this section applies were a living individual,
and sections 9, 10, 12 and 24 to 31 of that Act apply accordingly.
(3) In subsection (2) “relevant credit data” means information held on the Register which relates to a person to whom this section applies and which, if it were information relating to a living individual, would be personal data for the purposes of the Data Protection Acts 1988 and 2003 .
(4) This section applies to any person with an annual turnover of not more than €3,000,000 (and to whom sections 2, 4 and 6 of the Data Protection Act 1988 would not apply apart from this section).
(5) The Bank may, with the consent of the Minister, make regulations specifying for the purposes of subsection (4) how, and by reference to what year, annual turnover is to be calculated.
(6) The Bank shall notify the Data Protection Commissioner of any systemic problems identified by the Bank in relation to the obtaining, keeping, processing or use of information held on the Register.
(7) The Bank shall take such action (which may include action in cooperation with the Data Protection Commissioner) as appears to the Bank to be appropriate to eliminate or minimise any such systemic problems.
Annotations
Modifications (not altering text):
C4
References to Data Protection Commissioner construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), s. 14(2), commenced as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 175 of 2018.
Transfer of functions of Data Protection Commissioner to Commission
14. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the Data Protection Commissioner are transferred to the Commission.
(2) A reference in any enactment or instrument under an enactment to the Data Protection Commissioner or to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner shall be construed as a reference to the Commission.
...
C5
References to personal data and processing construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), ss. 165, 166, S.I. No. 174 of 2018.
Reference to personal data in enactment
165. Subject to this Act, a reference in any enactment to personal data within the meaning of the Act of 1988 shall be construed as including a reference to personal data within the meaning of—
(a) the Data Protection Regulation, and
(b) Part 5.
Reference to processing in enactment
166. Subject to this Act, a reference in any enactment to processing within the meaning of the Act of 1988 shall be construed as including a reference to processing within the meaning of—
(a) the Data Protection Regulation, and
(b) Part 5.
PART 3
Duties of Credit Information Providers
 Section 20
Section 20
Verification of identity of credit information subjects
20. (1) A credit information provider shall take such steps as are prescribed by regulations under subsection (2) to verify the identity of credit information subjects who—
(a) make credit applications to, or credit agreements with, the credit information provider, or
(b) propose to give, or give, a guarantee or indemnity in connection with a credit agreement with the credit information provider.
(2) The Bank shall, following consultation with the Data Protection Commissioner and with the consent of the Minister, make regulations prescribing such steps as it appears to the Bank are reasonable to require a credit information provider to take to verify the identity of credit information subjects referred to in subsection (1).
(3) Regulations under subsection (2) may make different provision in relation to—
(a) different classes of credit information providers, or
(b) different classes of credit information subjects.
Annotations
Modifications (not altering text):
C6
Reference to Data Protection Commissioner construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), s. 14(2), commenced as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 175 of 2018.
Transfer of functions of Data Protection Commissioner to Commission
14. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the Data Protection Commissioner are transferred to the Commission.
(2) A reference in any enactment or instrument under an enactment to the Data Protection Commissioner or to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner shall be construed as a reference to the Commission.
...
Editorial Notes:
E6
Power pursuant to section exercised (28.08.2019) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 20) (Verification of Identity of Credit Information Subjects) (Amendment) Regulations 2019 (S.I. No. 433 of 2019).
E7
Power pursuant to section exercised (30.06.2017 and 31.12.2017) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 20) (Verification of Identity of Credit Information Subjects) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 488 of 2016), in effect as per reg. 1(2), (3).
 Section 21
Section 21
Verification of accuracy of credit information
21. A credit information provider shall take reasonable steps to verify that the information which the credit information provider obtains from credit information subjects is accurate and complete.
 Section 22
Section 22
Informing credit information subject of suspected impersonation
22. (1) If a credit information provider reasonably believes that a credit information subject has been, or may have been, impersonated by any person, the credit information provider shall give to the credit information subject notice of that belief.
(2) The notice shall be given as soon as reasonably practicable and (in any event) not later than 24 hours after the credit information provider first believes that the credit information subject has been, or may have been, impersonated.
 Section 23
Section 23
Ensuring that credit information subjects are aware of rights and duties
23. A credit information provider shall ensure that credit information subjects who—
(a) make credit applications to, or credit agreements with, the credit information provider, or
(b) propose to give, or give, a guarantee or indemnity in connection with a credit agreement with the credit information provider,
are made aware of their rights and duties under this Act.
 Section 24
Section 24
Informing credit information subjects of duty to provide information
24. (1) A credit information provider shall include on its forms for the making of qualifying credit applications a notice stating that this Act requires the provision of information to the Bank relating to qualifying credit applications and qualifying credit agreements for entry on the Register.
(2) The Bank may, with the consent of the Minister, make regulations specifying the content and form of notices required by subsection (1).
Annotations
Editorial Notes:
E8
Power pursuant to section exercised (30.06.2017) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 24) (Notices) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 489 of 2016), in effect as pre reg. 1(2).
PART 4
Levy and Fees
 Section 25
Section 25
Levy on credit information providers
25. (1) The Bank may, with the consent of the Minister, make regulations prescribing a levy to be paid by credit information providers for the purpose of meeting expenses properly incurred by the Bank in the performance of its functions under this Act (and not otherwise met).
(2) Regulations under subsection (1) may in particular provide for—
(a) the amount, or methods of calculating the amount, of the levy;
(b) the period for which, and the dates by which, the levy is to be paid;
(c) penalties payable by a credit information provider who does not pay the levy on time;
(d) the keeping of records, and the making of returns to the Bank, in relation to the levy by credit information providers;
(e) the payment, collection and recovery of the levy;
(f) refunds of the levy.
(3) Regulations under subsection (1) may make different provision in relation to different classes of credit information providers.
(4) The Bank may enter into arrangements with any person in relation to the collection of the levy; and the amount of any levy payable is recoverable as a simple contract debt by proceedings in a court of competent jurisdiction by the Bank or any person with whom the Bank has entered into such arrangements.
(5) In this section “levy” does not include a fee.
 Section 26
Section 26
Fees
26. (1) The Bank may, with the consent of the Minister, make regulations prescribing fees to be paid for access to information held on the Register or being provided with a record of occasions on which access has been given to information held on the Register.
(2) Regulations under subsection (1) may in particular provide for—
(a) the amounts, or methods of calculating the amount, of fees;
(b) exemptions from the payment of fees;
(c) the payment, collection and recovery of fees;
(d) refunds of fees.
(3) Regulations under subsection (1) may not prescribe a fee for access to information by an individual under section 15(5) if the access is pursuant to the first application made by the individual in any year.
(4) Regulations under subsection (1) may make different provision in relation to different cases.
(5) The Bank may enter into arrangements with any person in relation to the collection of fees payable under regulations under subsection (1); and the amount of any fee so payable is recoverable as a simple contract debt by proceedings in a court of competent jurisdiction by the Bank or any person with whom the Bank has entered into such arrangements.
Annotations
Editorial Notes:
E9
Power pursuant to section exercised (3.08.2018) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 26) (Fees) (Amendment) Regulations 2018 (S.I. No. 348 of 2018).
E10
Power pursuant to section exercised (22.03.2018 and 31.12.2018) by Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 26) (Fees) Regulations 2018 (S.I. No. 91 of 2018), in effect on signature and as per reg. 1(2).
PART 5
Enforcement
 Section 27
Section 27
Enforcement
27. (1) The Central Bank Act 1942 is amended in Part 1 of Schedule 2 by inserting the following—
“
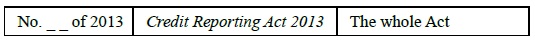
”.
(2) The amendment made by subsection (1) shall not have effect to cause a person to be a regulated financial services provider for the purposes of the Central Bank Act 1942, this Act or any other enactment.
(3) If the Bank considers that a credit information provider to whom this subsection applies has failed, or is failing, to comply with any obligation imposed by this Act, the Bank may direct the credit information provider to take specified steps to comply with the obligation.
(4) Subsection (3) applies to a credit information provider other than—
(a) a regulated financial services provider,
(b) NAMA, and
(c) a local authority.
(5) If the Bank considers that a credit information provider has failed, or is failing, to comply with a direction under subsection (3) the Bank may make an application to the High Court, and the High Court may, on such an application, make an order requiring the credit information provider to comply with the direction.
(6) If the Bank considers that NAMA has failed, or is failing, to comply with any obligation imposed by this Act, the Bank may give notice to the Minister, giving its reasons for so considering.
(7) On receipt of a notice under subsection (6), the Minister may direct NAMA to take specified steps to comply with the obligation and NAMA shall comply with the direction.
(8) If the Bank considers that a local authority has failed, or is failing, to comply with any obligation imposed by this Act, the Bank may give notice to the Minister and the Minister for the Environment, Community and Local Government, giving its reasons for so considering.
(9) On receipt of a notice under subsection (8), the Minister for the Environment, Community and Local Government may direct the local authority to take specified steps to comply with the obligation and the local authority shall comply with the direction.
 Section 28
Section 28
Enforcement: supplementary
28. (1) The provisions of a direction under section 27 have effect from the date specified in the direction in relation to them.
(2) A direction under section 27 shall set out—
(a) all terms of the direction, including any date specified as the date by which, or period specified as the period within which, any provision of the direction is to be complied with, and
(b) any incidental, supplementary or consequential provision for securing that the direction is fully complied with.
(3) On an application under section 27(5), the High Court may make any such interim or interlocutory order as it considers appropriate.
(4) An order under subsection (3) may include an order to take such ancillary or incidental steps as the High Court may consider appropriate to give full effect to the order.
 Section 29
Section 29
Offences
29. (1) A credit information provider who provides information required by this Act knowing it to be false or misleading commits an offence.
(2) A credit information provider who knowingly uses information to which access has been given under this Act for a purpose other than one permitted by this Act commits an offence.
(3) A person guilty of an offence under this section shall be liable—
(a) on summary conviction, to a class A fine or imprisonment for a term not exceeding 6 months or both, or
(b) on conviction on indictment, to a fine or imprisonment for a term not exceeding 5 years or both.
(4) Where an offence under this section committed by a body corporate is proved to have been committed with the consent or connivance, or to be attributable to any neglect on the part, of any person who was a director, manager, secretary or other officer of the body corporate or a person who was purporting to act in such a capacity, that person (as well as the body corporate) commits the offence and is liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
PART 6
Miscellaneous
 Section 30
Section 30
Power of Bank to produce credit scores and anonymised information
30. (1) The Bank may produce—
(a) credit scores and other analyses in relation to credit information subjects, and
(b) general reports, analyses and statistics from which credit information subjects cannot be identified.
(2) Where anything produced under subsection (1) is not held on the Register the Bank may sell it or publish it and sell copies of it.
 Section 31
Section 31
Accountability of Bank
31. (1) If the Governor or a Head of Function is requested by a Committee of the Oireachtas to—
(a) attend before the Committee, and
(b) provide the Committee with information relating to the Bank’s performance of its functions under this Act,
the Governor or Head of Function shall appear before the Committee and (subject to section 32) provide the Committee with such information relating to the Bank’s performance of its functions under this Act as the Committee requires.
(2) The reference in subsection (1) to a Committee of the Oireachtas is a reference to a Committee appointed by either House or by both Houses jointly to examine matters relating to the Bank and includes a subcommittee of such a Committee, but does not include the Committee on Members’ Interests of Dáil Éireann or the Committee on Members’ Interests of Seanad Éireann.
 Section 32
Section 32
Prohibition on unauthorised disclosure of information
32. (1) A person to whom this section applies shall not disclose confidential information received by the Bank in connection with the performance of the Bank’s functions under this Act.
(2) This section applies to every person who is or has been—
(a) the Governor,
(b) a member of the Commission,
(c) a Head of Function,
(d) the Registrar of Credit Unions,
(e) an officer or employee of the Bank or an agent of the Bank,
(f) employed as a consultant or auditor or in any other capacity by the Bank or an agent of the Bank.
(3) Subsection (1) does not prevent—
(a) the disclosure of information in compliance with this Act or as required or permitted by law or any enactment other than this Act,
(b) the disclosure of information to the Bank,
(c) the disclosure of information by or on behalf of the Bank to the Minister,
(d) the disclosure of information to the Data Protection Commissioner, or
(e) the disclosure of information which, in the opinion of a person to whom this section applies, may disclose the commission of an indictable offence to the Director of Corporate Enforcement, the Competition Authority, a member of the Garda Síochána or an officer of the Revenue Commissioners.
(4) A person who contravenes subsection (1) commits an offence.
(5) A person guilty of an offence under subsection (4) is liable—
(a) on summary conviction, to a class A fine or to imprisonment for a term not exceeding 12 months or both, or
(b) on conviction on indictment, to a fine not exceeding €30,000 or to imprisonment for a term not exceeding 5 years or both.
(6) In this section—
“confidential information” means information that is expressed by the Bank to be confidential, either as regards particular information or as regards information of a particular class;
“member of the Commission” shall be construed in accordance with section 2(1) of the Central Bank Act 1942.
Annotations
Modifications (not altering text):
C7
Reference to Data Protection Commissioner construed (25.05.2018) by Data Protection Act 2018 (7/2018), s. 14(2), commenced as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 175 of 2018.
Transfer of functions of Data Protection Commissioner to Commission
14. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the Data Protection Commissioner are transferred to the Commission.
(2) A reference in any enactment or instrument under an enactment to the Data Protection Commissioner or to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner shall be construed as a reference to the Commission.
...
C8
Reference to Competition Authority construed (31.10.2014) by Competition and Consumer Protection Act 2014 (29/2014), s. 39(2)(a), in effect as per subs. (4) and S.I. No. 367 of 2014.
Transfer of functions to Commission
39. (1) All functions that, immediately before the establishment day, were vested in the dissolved bodies are transferred to the Commission.
(2) References in any Act of the Oireachtas passed before the establishment day or in any instrument made before that day under an Act of the Oireachtas to—
(a) the National Consumer Agency, or
(b) the Competition Authority,
shall, on and after that day, be construed as references to the Commission.
...
 Section 33
Section 33
Prosecution of offences
33. Summary proceedings for an offence under section 29 or 32(4) may be brought and prosecuted by the Bank.
 Section 34
Section 34
Amendment of section 33AK of Central Bank Act 1942
34. Section 33AK of the Central Bank Act 1942 is amended in subsection (1)(h) by inserting “or is or was an agent engaged by the Bank” after “Bank”.
 Section 35
Section 35
Amendment of section 5 of Central Bank (Supervision and Enforcement) Act 2013
35. Subsections (2) and (3) of section 5 of the Central Bank (Supervision and Enforcement) Act 2013 shall be treated as having, and always having had, effect with the substitution of “to 4” for “to 3” in each place.

Number 45 of 2013
CREDIT REPORTING ACT 2013
REVISED
Updated to 28 August 2019
About this Revised Act
This Revised Act presents the text of the Act as it has been amended since enactment, and preserves the format in which it was passed.
Related legislation
This Act is not collectively cited with any other Act.
Annotations
This Revised Act is annotated and includes textual and non-textual amendments, statutory instruments made pursuant to the Act and previous affecting provisions.
An explanation of how to read annotations is available at
www.lawreform.ie/annotations.
Material not updated in this revision
Where other legislation is amended by this Act, those amendments may have been superseded by other amendments in other legislation, or the amended legislation may have been repealed or revoked. This information is not represented in this revision but will be reflected in a revision of the amended legislation if one is available.
Where legislation or a fragment of legislation is referred to in annotations, changes to this legislation or fragment may not be reflected in this revision but will be reflected in a revision of the legislation referred to if one is available.
A list of legislative changes to any Act, and to statutory instruments from 1972, may be found linked from the page of the Act or statutory instrument at
www.irishstatutebook.ie.
Acts which affect or previously affected this revision
• Markets in Financial Instruments Act 2018 (25/2018)
All Acts up to and including Judicial Council Act 2019 (33/2019), enacted 23 July 2019, were considered in the preparation of this revision.
Statutory instruments which affect or previously affected this revision
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 20) (Verification of Identity of Credit Information Subjects) (Amendment) Regulations 2019 (S.I. No. 433 of 2019)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 26) (Fees) (Amendment) Regulations 2018 (S.I. No. 348 of 2018)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 26) (Fees) Regulations 2018 (S.I. No. 91 of 2018)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 24) (Notices) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 489 of 2016)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 20) (Verification of Identity of Credit Information Subjects) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 488 of 2016)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 17) (Access to Central Credit Register) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 487 of 2016)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 11) (Provision of Information for Central Credit Register) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 486 of 2016)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 6) (Additional Personal Information) Regulations 2016 (S.I. No. 485 of 2016)
• Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Commencement) Order 2014 (S.I. No. 19 of 2014)
All statutory instruments up to and including Credit Reporting Act 2013 (Section 20) (Verification of Identity of Credit Information Subjects) (Amendment) Regulations 2019 (S.I. No. 433 of 2018), made 28 August 2019, were considered in the preparation of this revision.


